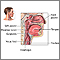
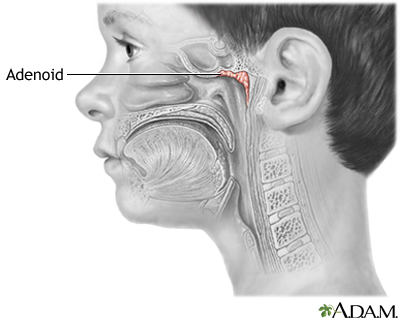
The adenoids are lymph tissues that sit in your upper airway between your nose and the back of your throat. They are similar to the tonsils.
Enlarged adenoids means this tissue is swollen.
Causes
Enlarged adenoids may be normal. They may grow bigger when the baby grows in the womb. The adenoids help the body prevent or fight infections by trapping bacteria and germs.
Infections can cause the adenoids to become swollen. The adenoids may stay enlarged even when you are not sick.
Symptoms
Children with enlarged adenoids often breathe through the mouth because the nose is blocked. Mouth breathing occurs mostly at night, but may be present during the day.
Mouth breathing may lead to the following symptoms:
- Bad breath
- Cracked lips
- Dry mouth
- Persistent runny nose or nasal congestion
Enlarged adenoids may also cause sleep problems. A child may:
- Be restless while sleeping
- Snore a lot
- Have episodes of not breathing during sleep (sleep apnea)
Children with enlarged adenoids may also have more frequent ear infections.
Exams and Tests
The adenoids cannot be seen by looking in the mouth directly. Your health care provider can see them by using a special mirror in the mouth or by inserting a flexible tube (called an endoscope) placed through the nose.
Tests may include:
- X-ray of the throat or neck
- Sleep study if sleep apnea is suspected
Treatment
Many people with enlarged adenoids have few or no symptoms and do not need treatment. Adenoids shrink as a child grows older.
Your provider may prescribe antibiotics or nasal steroid sprays if an infection develops.
Surgery to remove the adenoids (adenoidectomy) may be done if the symptoms are severe or persistent.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if your child has trouble breathing through the nose or other symptoms of enlarged adenoids.
Alternative Names
Adenoids - enlarged
Patient Instructions
Images
References
Chi DH, Tobey A. Otolaryngology. In: Zitelli BJ, McIntire SC, Nowalk AJ, Garrison J, eds. Zitelli and Davis' Atlas of Pediatric Physical Diagnosis. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 24.
Wetmore RF. Tonsils and adenoids. In: Kliegman RM, St. Geme JW, Blum NJ, Shah SS, Tasker RC, Wilson KM, eds. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 21st ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 411.
Review Date 8/5/2023
Updated by: Neil K. Kaneshiro, MD, MHA, Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.