



Table of Contents: 2012 JANUARY–FEBRUARY No. 384
Auston I. Quality Improvement Category Added to Health Services Research (HSR) PubMed Queries. NLM Tech Bull. 2012 Jan-Feb;(384):e4.
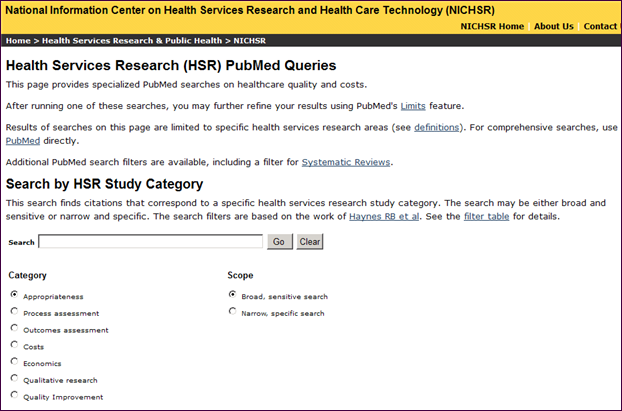
A new category relating to Quality Improvement (QI) has been added to the Health Services Research (HSR) PubMed Queries page (see Figure 1.)
Quality Improvement has received close attention during the past decade starting with the Institute of Medicine (IOM) landmark reports (To Err is Human: Building a Safer Health Care System (2000) and Crossing the Quality Chasm: A New Health System for the 21st Century (2001)) and more recently with the 2011 US Department of Health and Human Services National Quality Strategy (Report to Congress: National Strategy for Quality Improvement in Health Care, March 2011).
Physicians and the health care systems and communities in which they work are increasingly being expected to design, implement, and measure quality improvement interventions and processes that are focused on:
Quality Improvement, introduced as a MeSH heading in 2011, is defined as the attainment or process of attaining a new level of performance or quality. The new QI broad (sensitive) search query goes beyond the MeSH definition to retrieve studies that consider aspects of quality such as Clinical Competence, Outcomes and Process Assessment, Program Evaluation, Quality Indicators, and Quality Assurance. The new QI narrow (specific) search query retrieves studies that are methodologically rigorous and ready for application to practice and thus may not retrieve all studies relating to Quality Improvement. The purpose of these search queries is to help users quickly identify a set of relevant citations as a starting point, using the broad query when time allows or using the narrow query for a more manageable retrieval when there are time constraints. PubMed Related citations feature is useful for helping further identify relevant citations.
The search strategies (broad and narrow) for this category have been developed by Wilczynski NL, et al., as described in the following publication:
An additional resource is the special topic page on Quality available from the HSR Information Central (HSRIC) portal.
1 1 US Department of Health and Human Services. Report to Congress: National Strategy for Quality Improvement in Health Care. Washington (DC): The Department, March 2011 [cited 2011 Dec 1]. 26 p. Available from: //www.ahrq.gov/workingforquality/nqs/nqs2011annlrpt.htm.
By
Ione Auston
National Information Center for Health Sciences Research (NICHSR)