

|
||
| June 6, 2003 [posted] |
||
| PubMed CentralTM in Entrez |
||
|
The articles in PMC can be divided into two groups: regular PMC articles for which the full text is viewable directly in PMC, and PubLink articles for which full text is viewable only at the journal's own site. Regular PMC articles are always free. Most PubLink articles require a subscription for some time - usually a year or less - after they are published, and then are free to everyone. For a complete list of PMC journals, click on 'Journal List' in the sidebar of the PMC Entrez search page or go directly to //www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc//. The default PMC search is limited to articles that are free (including PubLink free). To include all PMC articles in your search, simply uncheck the Free full-text only box at the right of the search form (see Figure 1). Note that PMC indexes and searches the full text of all articles, even the PubLink articles which can be viewed only at the journal site. Articles in the early issues of some journals, for which the full text is available only as a PDF file, are the one exception. In these cases, PMC searches only the citation and abstract, just as PubMed does. 
The standard PMC search technique is labeled SmartSearch, reflecting the fact that it is based on an automated analysis of the title, abstract and full text of each article. SmartSearch is intended to increase the relevance of your search results. It does not search every word in the article as a simple full text search would do. To do that (search every word), uncheck the SmartSearch box on the search form (see Figure 1). In other respects, a standard PMC search works much like a PubMed search, automatically identifying, where practical, author names, journal titles, or known phrases in the input search string, and mapping search terms to MeSH terms. Although most PMC items have a corresponding PubMed citation (the exceptions are material such as book reviews, which are out of scope for PubMed), some of these citations may not be indexed for MEDLINE and therefore will not have MeSH terms attached in either PubMed or PMC. PMC also uses automated analysis to identify terms in an article that most likely are organism names. These names are then used to provide bi-directional links between the article and related records in the Entrez Taxonomy database. A search using a common name for an organism is translated to its scientific name whenever possible. For example, yeast → Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and mouse → Mus musculus. Organism names may also be searched directly via the [organism] field. To avoid a lot of false hits, the text analysis algorithm generally does not tag as an organism those terms that are commonly used in other contexts, e.g., Erica, or Paris.
Search Results
For an article with full text viewable directly in PMC, the citation on the search result page (see Figure 2) will include links to an [Abstract] if one exists, to the [Full Text], and in most cases to a [PDF] copy of the article. PubLink articles have only [PubLink] which takes you to a PMC 'abstract view' of the article where you can find a direct link to the full text at the journal site, as well as the details of when access restrictions on the full text will be lifted if it is not already free. 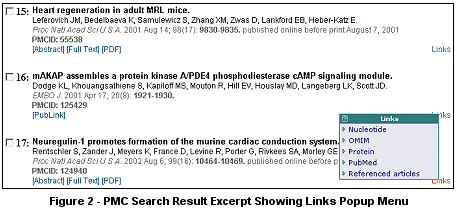
The Links popup menu (see Figure 2) associated with each article in a PMC search result page is similar to the PubMed Links menu. Special to PMC are a link to the Taxonomy database, which was mentioned earlier, and a Referenced articles link which produces a PubMed list of the articles in the References section of the PMC article. (Of course, the PubMed list will only include referenced articles that are cited in PubMed.) A Referenced articles link is not available from PMC articles in the early issues of some journals, for which the full text is available only in the form of a PDF file. As in PubMed, you can display a combined set of links for a group of articles by using the checkbox alongside each article to select the articles and then using the 'Display' option at the top of the result page (see Figure 3). 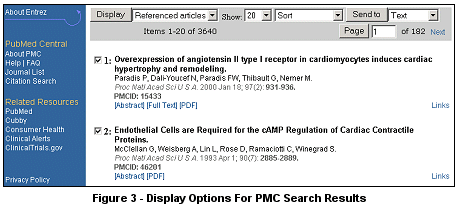
Search Limits
Preview/Index
Citation Searching 
Should I Search PubMed or PMC? In PubMed, setting the PubMed Central subset limit is the same as adding 'AND pubmed pmc local[sb]' to your search. Either way will give you only articles whose full text is viewable directly in PMC. Another way of extracting the PMC articles from a PubMed search result set is to display 'PMC Links' for the complete result set, using the Display button at the top of the results page. This will show the relevant citations on a PMC search results page, from which you can go directly to the full text. Be aware, though, that Entrez will truncate your secondary result set (in this case, the PMC citations) at 500 items. Displaying 'PMC Links' is equivalent to adding 'AND pubmed pmc[sb]' to your PubMed search. It selects all PMC articles, including PubLink articles that may still be available only to subscribers.
Want to Know More?
By Ed Sequeira Sequeira E. PubMed CentralTM in Entrez. NLM Tech Bull. 2003 May-Jun;(332):e3. |
||
 ubMed Central (PMC), NLM's digital archive of life sciences journal
articles, is now accessible as an Entrez database at
ubMed Central (PMC), NLM's digital archive of life sciences journal
articles, is now accessible as an Entrez database at