Alternative medicine refers to low- to no-risk treatments that are used instead of conventional (standard) ones. If you use an alternative treatment along with conventional medicine or therapy, it is considered complementary therapy.
Information
There are many forms of alternative medicine. They include acupuncture, chiropractic, herbal medicine, massage, magnetic waves, hypnosis, biofeedback, meditation, yoga, and tai-chi.
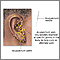
Acupuncture involves stimulating certain acupoints on the body using fine needles or other methods. How acupuncture works is not entirely clear. It is thought that acupoints lie near nerve fibers. When acupoints are stimulated, the nerve fibers signal the spinal cord and brain to release chemicals that relieve pain.
Acupuncture is an effective means of relieving pain, such as for back pain and headache pain. Acupuncture may also help relieve pain due to:
- Cancer
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Fibromyalgia
- Childbirth (labor)
- Musculoskeletal injuries (such as the neck, shoulder, knee, or elbow)
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Hypnosis is a focused state of concentration. With self-hypnosis, you repeat a positive statement over and over.
Hypnosis may help relieve pain for:
- After surgery or labor
- Arthritis
- Cancer
- Fibromyalgia
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- Migraine headache
- Tension headache
Both acupuncture and hypnosis are often offered by pain management centers in the United States. Other non-drug methods used at such centers include:
- Biofeedback
- Massage
- Relaxation training
- Physical therapy
Herbal medicine involves the use of various parts of plants. Many herbal medicines can interact with prescribed medicines, or can have other undesired effects. It is important to discuss all herbal therapies with your health care provider.
Some find magnetic waves helpful for healing, but these can interfere with certain medical devices and should be used only under direction of a medical provider during pregnancy.
Alternative Names
Acupuncture - pain relief; Hypnosis - pain relief; Guided imagery - pain relief
Images
References
Hecht FM. Complementary, alternative, and integrative medicine. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 34.
Hsu ES, Wu I, Lai B. Acupuncture. In: Benzon HT, Raja SN, Liu SS, Fishman SM, Cohen SP, eds. Essentials of Pain Medicine. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 60.
White JD. Complementary and alternative medicine. In: Niederhuber JE, Armitage JO, Kastan MB, Doroshow JH, Tepper JE, eds. Abeloff's Clinical Oncology. 6th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 31.
Review Date 11/9/2021
Updated by: Joseph V. Campellone, MD, Department of Neurology, Cooper Medical School at Rowan University, Camden, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David Zieve, MD, MHA, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.