Familial combined hyperlipidemia is a disorder that is passed down through families. It causes high cholesterol and high blood triglycerides.
Causes
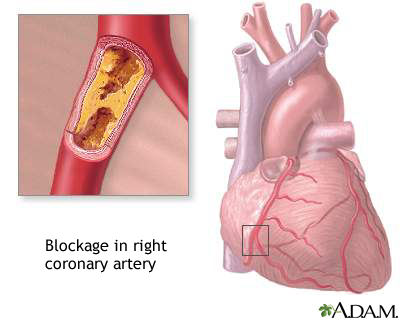
Familial combined hyperlipidemia is the most common genetic disorder that increases blood fats. It can cause early heart attacks.
Diabetes, alcoholism, and hypothyroidism make the condition worse. Risk factors include a family history of high cholesterol and early coronary artery disease.
Symptoms
In the early years, there may be no symptoms.
When symptoms appear, they may be due to impaired blood flow to parts of the body and include:
- Chest pain (angina) or other signs of coronary artery disease may be present at a young age.
- Cramping of one or both calves when walking.
- Sores on the toes that do not heal.
- Sudden stroke-like symptoms, such as trouble speaking, drooping on one side of the face, weakness of an arm or leg, and loss of balance.
People with this condition may develop high cholesterol or high triglyceride levels as teenagers. The condition may also be diagnosed when people are in their 20s and 30s. The levels remain high all during life. Those with familial combined hyperlipidemia have an increased risk of early coronary artery disease and heart attacks. They also have higher rates of obesity and are more likely to have glucose intolerance.
Exams and Tests
Blood tests will be done to check your levels of cholesterol and triglycerides. Tests will show:
- Increased LDL cholesterol
- Decreased HDL cholesterol
- Increased triglycerides
- Increased apolipoprotein B100
Genetic testing is available for one type of familial combined hyperlipidemia.
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to reduce the risk of atherosclerotic heart disease.
LIFESTYLE CHANGES
The first step is to change what you eat. Most of the time, you will try diet changes for several months before your doctor recommends medicines. Diet changes include lowering the amount of saturated fat and refined sugar.
Here are some changes you can make:
- Eat less beef, chicken, pork, and lamb
- Substitute low-fat dairy products for full-fat ones
- Avoid packaged cookies and baked goods that contain trans fats
- Reduce the cholesterol you eat by limiting egg yolks and organ meats
Counseling is often recommended to help people make changes to their eating habits. Weight loss and regular exercise may also help lower your cholesterol levels.

MEDICINES
If lifestyle changes do not change your cholesterol levels enough, or you are at very high risk for atherosclerotic heart disease, your health care provider may recommend that you take medicines. There are several types of drugs to help lower blood cholesterol levels.
The drugs work in different ways to help you achieve healthy lipid levels. Some are better at lowering LDL cholesterol, some are good at lowering triglycerides, while others help raise HDL cholesterol.
The most commonly used, and most effective drugs for treating high LDL cholesterol are called statins. They include lovastatin (Mevacor), pravastatin (Pravachol), simvastatin (Zocor), fluvastatin (Lescol), atorvastatin (Lipitor), rosuvastatin (Crestor), and pitivastatin (Livalo).
Other cholesterol-lowering medicines include:
- Bile acid-sequestering resins.
- Ezetimibe.
- Fibrates (such as gemfibrozil and fenofibrate).
- Nicotinic acid.
- PCSK9 inhibitors, such as alirocumab (Praluent) and evolocumab (Repatha) These represent a newer class of drugs to treat high cholesterol.
Outlook (Prognosis)
How well you do depends on:
- How early the condition is diagnosed
- When you start treatment
- How well you follow your treatment plan
Without treatment, heart attack or stroke may cause early death.
Even with medicine, some people may continue to have high lipid levels that increase their risk for heart attack.
Possible Complications
Complications may include:
- Early atherosclerotic heart disease
- Heart attack
- Stroke
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Seek medical care right away if you have chest pain or other warning signs of a heart attack.
Contact your provider if you have a personal or family history of high cholesterol levels.
Prevention
A diet that is low in cholesterol and saturated fat may help to control LDL levels in people at high risk.
If someone in your family has this condition, you may want to consider genetic screening for yourself or your children. Sometimes, younger children may have mild hyperlipidemia.
It is important to control other risk factors for early heart attacks, such as smoking.
Alternative Names
Multiple lipoprotein-type hyperlipidemia
References
Genest J, Mora S, Libby P. Lipoprotein disorders and cardiovascular disease. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD, eds. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 27.
Robinson JG. Disorders of lipid metabolism. In: Goldman L, Schafer AI, eds. Goldman-Cecil Medicine. 26th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2020:chap 195.
Review Date 5/8/2022
Updated by: Michael A. Chen, MD, PhD, Associate Professor of Medicine, Division of Cardiology, Harborview Medical Center, University of Washington Medical School, Seattle, WA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.