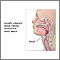
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a problem in which your breathing pauses during sleep. This occurs because of narrowed or blocked airways.
Causes
When you sleep, all of the muscles in your body become more relaxed. This includes the muscles that help keep your throat open so air can flow into your lungs.
Normally, your throat remains open enough during sleep to let air pass by. Some people have a narrow throat. When the muscles in their upper throat relax during sleep, the tissues close in and block the airway. This stop in breathing is called apnea.
Loud snoring is a telltale symptom of OSA. Snoring is caused by air squeezing through the narrowed or blocked airway. Not everyone who snores has sleep apnea though.
 Watch this video about:Snoring
Watch this video about:SnoringOther factors also may increase your risk:
- A lower jaw that is short compared to your upper jaw
- Certain shapes of the roof of your mouth (palate) or airway that cause it to collapse more easily
- Large neck or collar size, 17 inches (43 centimeters) or more in men and 16 in (41 cm) or more in women
- Large tongue, which may fall back and block the airway
- Obesity
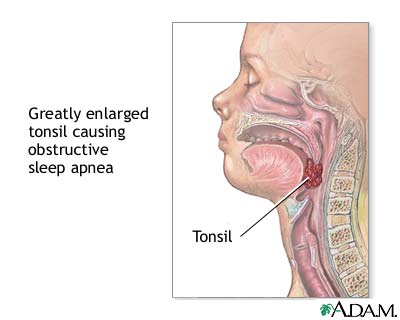
- Large tonsils and adenoids that can block the airway
Sleeping on your back can also cause your airway to become blocked or narrowed.
Central sleep apnea is a different sleep disorder during which breathing also can stop. It occurs when the brain temporarily stops sending signals to the muscles that control breathing.
Symptoms
If you have OSA, you usually begin snoring heavily soon after falling asleep.
- The snoring often becomes very loud.
- Snoring may be interrupted by a long silent period while your breathing stops.
- The silence is followed by a loud snort and gasp, as you attempt to breathe.
- This pattern repeats throughout the night.
Most people with OSA do not know their breathing starts and stops during the night. Usually, a sleep partner or other family members hear the loud snoring, gasping, and snorting. Snoring can be loud enough to hear through walls. Sometimes, people with OSA wake up gasping for air.
People with sleep apnea may:
- Wake up unrefreshed in the morning
- Feel sleepy or drowsy throughout the day
- Act grumpy, impatient, or irritable
- Be forgetful
- Fall asleep while working, reading, or watching TV
- Feel sleepy while driving, or even fall asleep while driving
- Have hard-to-treat headaches
Other problems that may occur include:
- Depression
- Hyperactive behavior, especially in children
- Difficult to treat high blood pressure
- Headaches, especially in the morning
Exams and Tests
Your health care provider will take your medical history and do a physical exam.
- Your provider will check your mouth, neck, and throat.
- You may be asked about daytime sleepiness, how well you sleep, and bedtime habits.
You will need to have a sleep study to confirm OSA. This testing can be done in your home or in a sleep lab.
Other tests that may be performed include:
- Arterial blood gases
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Echocardiogram
- Pulse oximetry
- Thyroid function studies
Treatment
Treatment helps keep your airway open while you sleep so your breathing does not stop.
Lifestyle changes may help relieve symptoms in people with mild sleep apnea, such as:
- Avoid alcohol or medicines that make you sleepy before bedtime. They can make symptoms worse.
- Avoid sleeping on your back.
- Lose excess weight.
Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) devices work best to treat obstructive sleep apnea in most people.
- You wear a mask over your nose or over your nose and mouth while you sleep.
- The mask is connected by a hose to a small machine that sits at the side of your bed.
- The machine pumps air under pressure through the hose and mask and into your airway while you sleep. This helps keep your airway open.
It can take some time to get used to sleeping with CPAP therapy. Good follow-up and support from a sleep center can help you overcome any problems using CPAP.
Dental devices may help some people. You wear them in your mouth while you sleep to keep your jaw forward and the airway open.
Other treatments may be available, but there is less evidence that they work. It is best to talk with a provider who specializes in sleep problems before trying them.
Surgery may be an option for some people. It is often a last resort if other treatments did not work and you have severe symptoms. Surgery may be used to:
- Remove extra tissue at the back of the throat.
- Correct problems with the structures in the face.
- Create an opening in the windpipe to bypass the blocked airway if there are physical problems.
- Remove the tonsils and adenoids.
- Implant a pacemaker-like device that stimulates the muscles of the throat to stay open during sleep.
Surgery may not completely cure OSA and may have long-term side effects.
Outlook (Prognosis)
If not treated, sleep apnea may cause:
- Anxiety and depression
- Loss of interest in sex
- Poor performance at work or school
Daytime sleepiness because of sleep apnea can increase the risk of:
- Motor vehicle accidents from driving while sleepy
- Industrial accidents from falling asleep on the job
In most cases, treatment completely relieves symptoms and problems from sleep apnea.
Possible Complications
Untreated OSA may lead to or worsen heart disease, including:
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You feel very tired and sleepy during the day
- You or your family notice symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea
- Symptoms do not improve with treatment, or new symptoms develop
Alternative Names
Sleep apnea - obstructive - adults; Apnea - obstructive sleep apnea syndrome - adults; Sleep-disordered breathing - adults; OSA - adults
Images
References
Greenberg H, Scharf MT, West S, Rajan P, Scharf SM. Obstructive sleep apnea: clinical features, evaluation, and principles of management. In: Kryger M, Roth T, Goldstein CA, Dement WC, eds. Principles and Practice of Sleep Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 131.
Kimoff RJ, Kaminska M, Pamidi S. Obstructive sleep apnea. In: Broaddus VC, Ernst JD, King TE, et al, eds. Murray and Nadel's Textbook of Respiratory Medicine. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 120.
Patil SP, Ayappa IA, Caples SM, Kimoff RJ, Patel SR, Harrod CG. Treatment of adult obstructive sleep apnea with positive airway pressure: an American Academy of Sleep Medicine clinical practice guideline. J Clin Sleep Med. 2019;15(2):335-343. PMID: 30736887 pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30736887/.
Redline S. Sleep-disordered breathing and cardiac disease. In: Libby P, Bonow RO, Mann DL, Tomaselli, GF, Bhatt DL, Solomon SD. Braunwald's Heart Disease: A Textbook of Cardiovascular Medicine. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 89.
Review Date 1/9/2023
Updated by: Allen J. Blaivas, DO, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care, and Sleep Medicine, VA New Jersey Health Care System, Clinical Assistant Professor, Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, East Orange, NJ. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Internal review and update on 02/12/2024 by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.