Vaginal discharge refers to secretions from the vagina. The discharge may be:
- Thick, pasty, or thin
- Clear, cloudy, bloody, white, yellow, or green
- Odorless or have a bad odor
Itching of the skin of the vagina and the surrounding area (vulva) may be present along with vaginal discharge. It can also occur on its own.
Causes
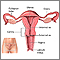
Glands in the cervix and the walls of the vagina normally produce clear mucus. This is very common among women of childbearing age.
- These secretions may turn white or yellow when exposed to the air.
- The amount of mucus produced varies during the menstrual cycle. This happens due to the change in hormone levels in the body.
The following factors can increase the amount of normal vaginal discharge:
- Ovulation (the release of an egg from your ovary in the middle of menstrual cycle)
- Pregnancy
- Sexual excitement
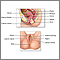
Different types of infections may cause itching or an abnormal discharge in the vagina. Abnormal discharge means abnormal color (brown, green), and odor. It is associated with itching or irritation.
These include:
- Infections spread during sexual contact. These include chlamydia, gonorrhea (GC), and trichomoniasis.
- Vaginal yeast infection, caused by a fungus.
- Normal bacteria that live in the vagina overgrow and cause a gray discharge and fishy odor. This is called bacterial vaginosis (BV). BV is not spread through sexual contact.
Other causes of vaginal discharge and itching may be:
- Menopause and low estrogen levels. This may lead to vaginal dryness and other symptoms (atrophic vaginitis).
- Forgotten tampon or foreign body. This may cause a foul odor.
- Chemicals found in detergents, fabric softeners, feminine sprays, ointments, creams, douches, and contraceptive foams or jellies or creams. This may irritate the vagina or the skin around the vagina.
Less common causes include:
- Cancer of the vulva, cervix, vagina, uterus, or fallopian tubes
- Skin conditions, such as desquamative vaginitis and lichen planus
Home Care
Keep your genital area clean and dry when you have vaginitis. Make sure to seek help from health care provider for the best treatment.
- Avoid soap and just rinse with water to clean yourself. Using a spray bottle to wash with water after urination may be helpful.
- Soaking in a warm but not hot bath may help your symptoms. Dry thoroughly afterward. Rather than using a towel to dry, you may find that gentle use of warm or cold air from a hair dryer may result in less irritation than the use of a towel.
Avoid douching. Many women feel cleaner when they douche, but it may actually worsen symptoms because it removes healthy bacteria that line the vagina. These bacteria help protect against infection.
Avoid current popular trends like vaginal steaming which may increase risk of vaginal infections.
Other tips are:
- Avoid using hygiene sprays, fragrances, or powders in the genital area.
- Use pads and not tampons while you have an infection.
- If you have diabetes, keep your blood sugar levels in good control.
Allow more air to reach your genital area. You can do this by:
- Wearing loose-fitting clothes and not wearing panty hose.
- Wearing cotton underwear (rather than synthetic), or underwear that has a cotton lining in the crotch. Cotton increases air flow and decreases moisture buildup.
- Not wearing underwear.
Girls and women should also:
- Know how to properly clean their genital area while bathing or showering.
- Wipe properly after using the toilet -- always from front to back.
- Wash thoroughly before and after using the bathroom.
Always practice safe sex. Use condoms to avoid catching or spreading infections.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider right away if:
- You have vaginal discharge
- You have fever or pain in your pelvis or belly area
- You may have been exposed to STIs
Changes that could indicate a problem such as infection include:
- You have a sudden change in the amount, color, odor, or consistency of discharge.
- You have itching, redness, and swelling in the genital area.
- You think that your symptoms may be related to a medicine you are taking.
- You are concerned that you may have a STI or you are unsure if you have been exposed.
- You have symptoms that get worse or last longer than 1 week despite home care measures.
- You have blisters or other sores on your vagina or vulva.
- You have burning with urination or other urinary symptoms. This may mean that you have a urinary tract infection.
What to Expect at Your Office Visit
Your provider will:
- Ask about your medical history
- Perform a physical exam including a pelvic exam
Tests that may be performed include:
- Cultures of your cervix
- Examination of vaginal discharge under the microscope (wet prep)
- Pap test
- Skin biopsies of the vulvar area
Treatment depends on the cause of your symptoms.
Alternative Names
Pruritus vulvae; Itching - vaginal area; Vulvar itching
References
Clutterbuck DJ. Sexually transmitted infections. In: Penman ID, Ralston SH, Strachan MWJ, Hobson RP, eds. Davidson's Principles and Practice of Medicine. 24th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2023:chap 15.
Eckert LO, Lentz GM. Genital tract infections: vulva, vagina, cervix, toxic shock syndrome, endometritis, and salpingitis. In: Gershenson DM, Lentz GM, Valea FA, Lobo RA, eds. Comprehensive Gynecology. 8th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 23.
Seller RH, Symons AB. Vaginal discharge and itching. In: Seller RH, Symons AB, eds. Differential Diagnosis of Common Complaints. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 33.
Review Date 8/23/2023
Updated by: LaQuita Martinez, MD, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Emory Johns Creek Hospital, Alpharetta, GA. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team.