This is a preview of updates coming to the Technical Bulletin's website in April 2026. Return to current site.
Read more about the modernization release schedule in this announcement.
Comment via the yellow feedback button in the lower right hand corner of the page. Contact the NLM Help Desk with any questions or concerns.
This is archived content.
Links may have become inactive over time. Visit Archive-It to find the original published layout.
MeSH on Demand Update: How to Find Citations Related to Your Text
Cho D. MeSH on Demand Update: How to Find Citations Related to Your Text. NLM Tech Bull. 2014 Jul-Aug;(399):e4.
August 22, 2014 [posted]
In May 2014, NLM introduced MeSH on Demand, a Web-based tool that suggests MeSH terms from your text such as an abstract or grant summary up to 10,000 characters using the MTI (Medical Text Indexer) software. For more background information, see the article, MeSH on Demand Tool: An Easy Way to Identify Relevant MeSH Terms.
New Feature
A new MeSH on Demand feature displays the PubMed ID (PMID) for the top ten related citations in PubMed that were also used in computing the MeSH term recommendations.
To access this new feature start from the MeSH on Demand homepage (see Figure 1), add your text, such as a project summary, into the box labeled "Text to be Processed." Then, click the "Find MeSH Terms" button.
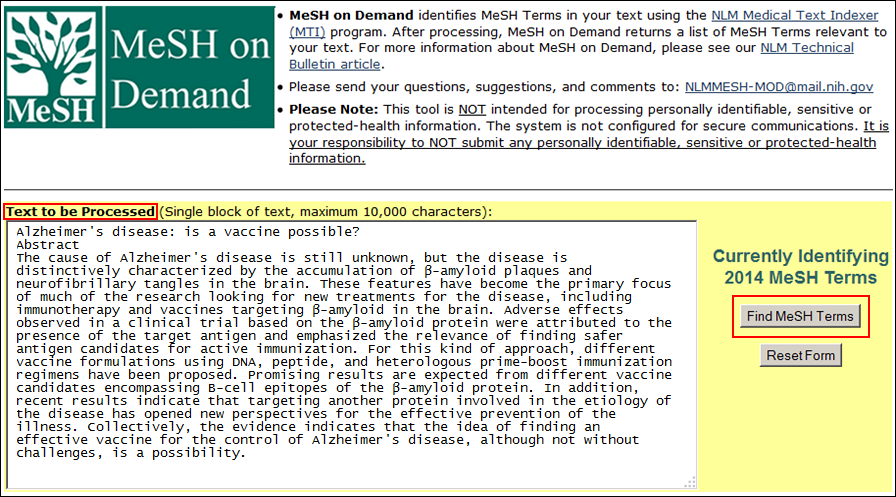
Figure 1: The MeSH on Demand homepage.
The MeSH on Demand results page is organized into three sections (see Figure 2):
- Section 1: Original Input Text (with the length of the input text)
- Section 2: MeSH Terms with Links to the MeSH Browser
- Section 3: Top Ten PubMed/MEDLINE Citations Related to Your Text
MeSH on Demand lists the top ten related citation PMIDs from PubMed/MEDLINE. Each PMID is hyperlinked to that citation in PubMed.
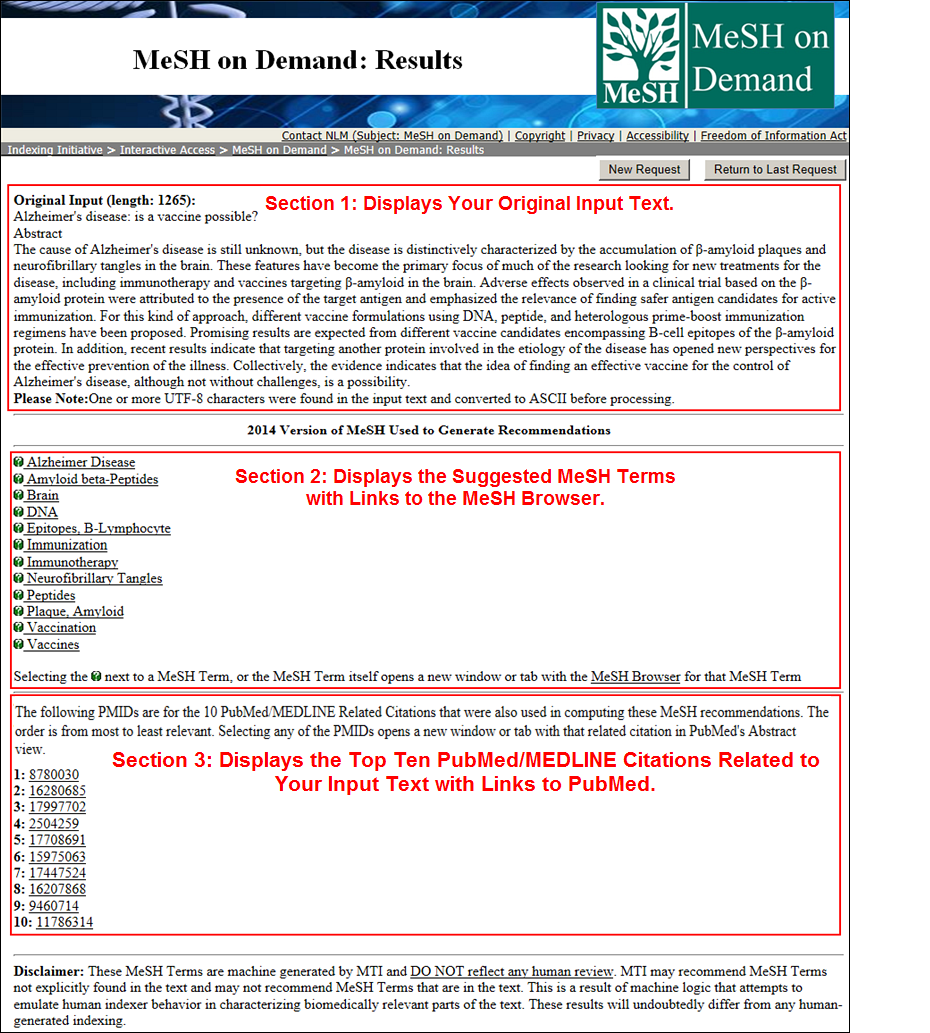
Figure 2: The MeSH on Demand results page.
Suggestions and Feedback
This new feature in MeSH on Demand is a result of user feedback received from our initial MeSH on Demand release. We encourage users to continue to send questions, suggestions, and comments to: NLMMESH-MOD@mail.nih.gov


