Homology: Orthologs and Paralogs
Homology refers to biological features including genes and their products that are descended from a feature present in a common ancestor. Homologous features such as genes are referred to as homologs (or homologues if you follow British spelling).
Homologous genes become separated in evolution in two different ways: separation of two populations with the ancestral gene into two species or gene duplication of the ancestral gene within a lineage.
- Genes separated by speciation are called orthologs.
- Genes separated by gene duplication events are called paralogs.
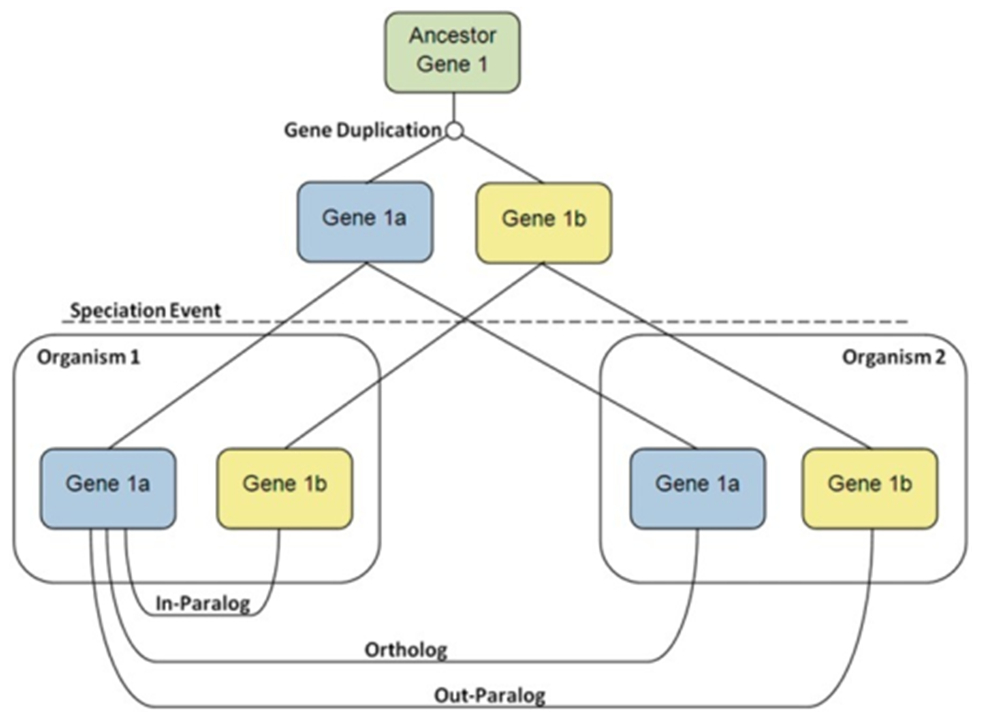
The process is shown in the diagram below.
Gene 1 in the ancestral species undergoes a duplication event generating Gene 1a and Gene 1b. The ancestral species splits into two species, each with its own copy of Gene 1a and Gene 1b
- Gene 1a in species one is the ortholog of Gene 1a in species two.
- Gene 1a and Gene 1b are paralogs.
- All four genes are homologs.